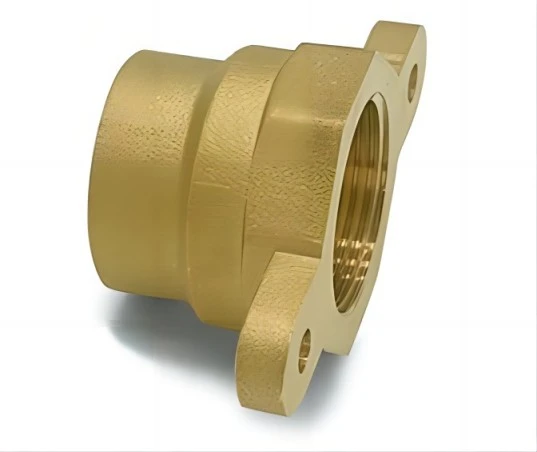
Why Using Sand Casting Service?
Sand casting services offer several advantages that make them a preferred choice for producing metal parts in various industries. Some of the key advantages include:
| Advantage | Descriptions |
| Versatility | Sand casting is versatile and can be used to produce a wide range of part sizes, shapes, and complexities. It is suitable for both small and large components, from simple to highly intricate designs. |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Sand casting is relatively economical compared to other casting methods, especially for low to medium volume production runs. The tooling costs are typically lower, and the process is well-suited for producing complex shapes without the need for expensive equipment. |
| Design Flexibility | Sand casting allows for intricate designs and complex geometries, making it ideal for parts with irregular shapes, undercuts, and internal features. This flexibility in design enables engineers to optimize part performance and functionality. |
| Material Variety | Sand casting can be used with a wide range of metals and alloys, including ferrous and non-ferrous materials such as aluminum, brass, bronze, iron, and steel. This versatility in material selection allows manufacturers to choose the most suitable alloy for specific applications. |
| Short Lead Times | Sand casting typically has shorter lead times compared to other manufacturing processes, making it suitable for projects with tight deadlines or urgent requirements. The process is relatively simple and can be scaled up or down to meet production needs quickly. |
| Scalability | Sand casting is easily scalable and can accommodate different production volumes, from prototype development to mass production. It is well-suited for both small batches and large-scale manufacturing, providing flexibility to adapt to changing demand. |
| Surface Finish | With proper mold design and finishing techniques, sand casting can achieve excellent surface finishes on cast parts. This reduces the need for additional machining or surface treatments, saving time and costs in the production process. |
| Proven Reliability | Sand casting is a well-established and reliable manufacturing process with a long history of successful applications across various industries. It offers consistent results and high-quality castings, providing confidence to manufacturers and end-users alike. |
The advantages of sand casting services make them a preferred choice for producing metal parts in a wide range of industries, including automotive, aerospace, construction, and manufacturing.
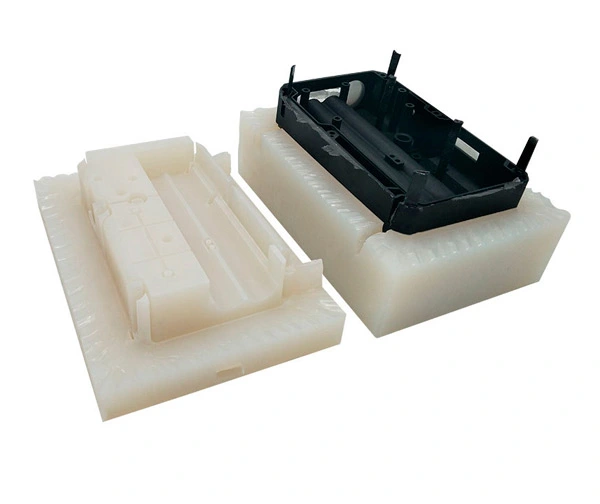
How Does Sand Casting Work?
There are mainly 9 steps of sand casting process:
1. Pattern Creation: The process begins with the creation of a pattern, which is a replica of the final part to be cast. Patterns can be made from various materials such as wood, metal, or plastic. The pattern is typically slightly larger than the final part to accommodate shrinkage during cooling.
2. Mold Preparation: Two halves of a mold are created using the pattern. The mold is made of sand mixed with a binder to hold its shape. The pattern is placed in one half of the mold, and then the other half is positioned on top to create a complete mold cavity.
3. Pattern Removal: Once the mold is formed around the pattern, the pattern is removed, leaving behind a cavity in the sand mold that matches the shape of the desired part.
4. Core Placement (optional): For parts with internal features or cavities, sand cores may be inserted into the mold to create the desired shape.
5. Mold Assembly: The two halves of the mold are securely clamped together, often with the help of alignment pins or screws. Channels called gates and runners are formed in the sand to allow molten metal to flow into the mold cavity during pouring and to facilitate the escape of air and gases.
6. Pouring: Molten metal is poured into the mold cavity through the gating system. The metal is typically heated in a furnace to the appropriate temperature before pouring to ensure proper flow and casting quality.
7. Solidification: The molten metal fills the mold cavity and solidifies as it cools. The cooling rate can affect the microstructure and properties of the final casting.
8. Cooling and Shakeout: After the metal has solidified, the mold is allowed to cool before the casting is removed from the sand. The sand mold is typically broken away from the casting using vibration or mechanical methods in a process known as shakeout.
9. Finishing: The casting may undergo various finishing operations to achieve the desired surface finish, dimensions, and mechanical properties.


 EN
EN
 jp
jp  ko
ko  fr
fr  de
de  es
es  it
it  pt
pt  tr
tr  ar
ar  iw
iw